Difference between revisions of "HF Aeronautical Communications"
From The RadioReference Wiki
(New page: == Aircraft on HF == Aircraft utilize HF communications when VHF (Line of Sight) communications is not sufficient. The primary usage of HF is for Trans-oceanic flights. Trans-oceanic flig...) |
|||
| Line 220: | Line 220: | ||
H+00 & H+30 | H+00 & H+30 | ||
| − | == | + | ==What is HFDL?== |
HFDL is a HF data link protocol, defined in [http://www.arinc.com ARINC] spec 635-3. The HFDL service is operated by ARINC as GLOBALink service through a worldwide network of HF stations. | HFDL is a HF data link protocol, defined in [http://www.arinc.com ARINC] spec 635-3. The HFDL service is operated by ARINC as GLOBALink service through a worldwide network of HF stations. | ||
Revision as of 16:21, 28 November 2009
Contents
Aircraft on HF
Aircraft utilize HF communications when VHF (Line of Sight) communications is not sufficient. The primary usage of HF is for Trans-oceanic flights. Trans-oceanic flights communicate with ground stations via HF for position reports and other purposes. Another utilization of HF communications is for HFDL or High Frequency DataLink. Finally Military Aircraft (MILCRAFT) utilize HF for operational and training.
- MWARA frequencies - Aircraft use these stations to communicate over water when out of VHF radio range.
- MWARA Frequency map on HFunderground
VOLMET
VOLMET, or meteorological information for aircraft in flight, is the term applied to a worldwide network of radio stations that broadcast TAF, SIGMET and METAR reports on shortwave frequencies. Reports are sent using automated voice transmissions, in the upper sideband or J3E mode. As the name suggests, pilots on international air routes use these transmissions to determine what procedures to use for descent, approach, and landing, such as a visual approach or an instrument approach and the correct STAR. The actual term comes from the contraction of 2 French words, loosely translated as 'Flying Weather'.
The VOLMET network divides the world into specific regions, and individual VOLMET stations in each region broadcast weather reports for specific groups of air terminals in their region at specific times, coordinating their transmission schedules so as not to interfere with one another. Schedules are determined in intervals of five minutes, with one VOLMET station in each region broadcasting reports for a fixed list of cities in each interval. These schedules repeat every hour.
Use for Propagation
VOLMET Broadcasts are great for propagation measuring, since they have set schedules and frequencies all over the world and can give an clear indication of when propagation is strong or weak in areas.
VOLMET Station Frequencies and Times
ANCHORAGE 2863, 6679, 8828, 13282 H+25-30 & H+55-00 ANDERSEN 18002 2200-0700Z 13201 2000-0900Z 11176 H24 8967 H24 6738 0700-2200Z 4721 0900-2000Z H+15 & H+45 ASUNCION 5601 0905-2315Z 10067 H+05 H+15 AUCKLAND 6679 H24 8828 H24 13282 H24 H+20+H-25 BANGKOK 11387 2310-1145Z 6676 H24 H+10-15 & H+40-45 BANGKOK INTL 2965 1210-2245Z H+10-15 & H+40-45 BEIJING *13285 0000-1600Z *8849 **5673 **3458 H+15 - H+20 H+45 - H+50 *Day **Ngt BEIRUT 3001 H24 5561 H24 H+15 & H+45 BRAZZAVILLE* 10057 0700-2000Z H+00 & H+25 10057 2000-0700Z H+30 & H+55 *English and French language CALCUTTA 11387 H24 6676 (0300-1300Z) 2965 (1300-0300Z) H+05-10 & H+35-40 COMODORO RIVADAVIA RADIO 4675 0900-2400Z 8938 0900-2400Z H+30 & H+40 CORDOBA RADIO 5475 H24 H+25 8952 H24 H+25 DAMASCUS 2992 H24 5667 H24 8918 H24 13312 H24 H+30 & Special H+00 & Special H+00 & Special EDMONTON MILITARY 6753 2300-1200Z EVEN HRS+20 15035 1200-2300Z, ODD HRS+20 EZEIZA RADIO 2881 H24 5601 H24 11369 H24 H+15 & H+01 GANDER 3485 H24 H+20-25 6604 H24 10051 H24 H+25-30 13270 H24 H+50-55 & H+55-60 HONG KONG 2863 H24 H+15-20 6679 H+45-50 8828 13282 HONOLULU 2863 H24 H+00-05 6679 H24 H+30-35 8828 H24 13282 H24 H+05-10 & H+35-40 H+25-30 & H+55-60 KARACHI 6680 H24 3432 1500-0130Z 10017 0130-1500Z H+15 & H+45 LAJES 13244 1000-2100Z 8967 H24 6750 H24 H+00 & H+30 8070 1015-2315 H+15 MACDILL 18019 0900-2400Z 13244 0900-2400Z 11246 H24 8993 H24 6750 0001-0900Z 4746 0001-0900Z H+15 & H+45 MONTEVIDEO 8873 1000-2100Z H+15 AFST CARRASCO INTL. 5451 11387 H24 6676 H24 2965 H+25-30 & H+55-00 NEW YORK 3485 H24 6604 H24 H+00-05 10051 H24 13270 H24 H+05-20 & H+30-50 OAKLAND 2863 H24 H+05-10 6679 H24 H+35-40 8828 H24 13282 H24 RESISTENCIA RADIO 4675 H24 H+20 & H+50 ROYAL AIR FORCE 5450 H24 11253 H24 Broadcast of airfields is twice an hour in slot times allotted as follows: 00/30, 06/36, 12/42, 18/48, 24/54 SALTA RADIO 5475 H24 H+15 & H+45 SHANNON 3413 SS-SR H+00 8957 H24 5505 H24 13264 SR-SS H+05, H+10, H+15, H+20, H+30, H+35, H+40, H+45, H+50 SINGAPORE 6676 1230-2230Z 11387 2230-1230Z H+20 & H+50 SYDNEY 6676 H24 11387 H24 H+00 & H+30 TAIWAN 2880 H24 5010 H+07 12400 TRENTON (MILITARY) 15034 1000-0000Z 6754 2300-1100Z H+10-15, H+15-20, H+20-25, H+25-30 TOKYO 2863 H24 6679 H+10-15 & H+40-45 8828 13282 YOKOTA 18002 0001-0800Z 13201 2100-1000Z 11236 H24 8967 H24 6738 0800-2400Z 4747 1000-2100Z H+00 & H+30
What is HFDL?
HFDL is a HF data link protocol, defined in ARINC spec 635-3. The HFDL service is operated by ARINC as GLOBALink service through a worldwide network of HF stations.
The name is somewhat misleading, as HFDL actually describes a class of data signals; it is also referred to as HF ACARS.
- Transmissions on HF are in USB on a sub carrier of 1440 Hz with a symbol speed of 1800 baud.
- Modulation is 2-PSK, 4-PSK or 8-PSK with effective bit rates of 300, 600, 1200 or 1800 bits/sec.
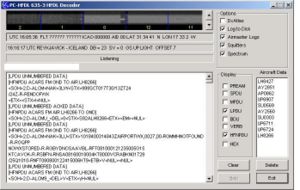
PC-HFDL
PC-HFDL is a Windows software to decode HFDL data traffic and has been written by Charles Brain. Just feed the HF receiver speaker's output into the soundcard of a Windows PC. It can be downloaded from the HFDL Yahoo group listed below.
The best monitoring results will be achieved with the following PC-HFDL settings:
- PREAM ON - to control the audio offset of the receiver
- SPDU OFF - only needed temporarily ON to see the squitters of a new unknown ground station
- MPDU ON - see the MPDU packets
- LPDU ON - see the LPDUs within the MPDUs
- BDU ON - see the BDUs
- VERB ON - see more details
- HFNPDU ON - see the routine position reports
- HEX OFF - only needed for debugging purposes
So in short, with all options ON except SPDU and HEX, the complete session can be seen: LOG-ON of the aircraft to the ground station giving its 24bit ICAO-ID, the assignment of the 1byte sequence ID number to the given ICAO-ID by the ground station referenced in all subsequent traffic, clear distinction of MPDU packets containing more than just one LPDU, and full traffic details.
The HFDL Yahoo group can be found here. Version 2.042 (which is Vista compatible) can be downloaded from this stub page
Other Packages known to support HFDL
- Hoka Code30/A
- Hoka Code 300/A
- Hoka 300-32
- Monteria Centurion
- Skysweeper
- Wavecom W61PC
- Wavecom W61LAN
Frequencies in Use
Thanks to MT Utility World which had the text link. New entries are in bold
ARINC System Table 34
| Node ID | Xmtr Name | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 | 15 | 16 | 17 | 18 | 19 | 20 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 01 | San Francisco CA | 21934 | 17919 | 13276 | 11327 | 10081 | 8927 | 6559 | 5508 | 4672 | 2947 | ||||||||||
| 02 | Molokai, HI | 21937 | 21928 | 17934 | 17919 | 13324 | 13312 | 13276 | 11348 | 11312 | 10081 | 8936 | 8912 | 6565 | 6559 | 5514 | 5463 | 4687 | 3434 | 3019 | 2947 |
| 03 | Reykjavik, ISL | 17985 | 15025 | 11184 | 8977 | 6712 | 5720 | 3900 | 3116 | ||||||||||||
| 04 | Riverhead, NY | 21934 | 21931 | 17952 | 17934 | 17919 | 13276 | 11387 | 11354 | 11315 | 10027 | 8912 | 8885 | 8831 | 6661 | 6652 | 6646 | 5652 | 5523 | 3428 | 3410 |
| 05 | Auckland, NZL | 21949 | 17916 | 13351 | 11327 | 10084 | 8921 | 6535 | 5583 | 3404 | 3016 | ||||||||||
| 06 | Hat Yai, THA | 21949 | 17928 | 13270 | 10066 | 8825 | 6535 | 5655 | 4687 | 3470 | |||||||||||
| 07 | Shannon, IRL | 11384 | 10081 | 8942 | 8843 | 6532 | 5547 | 3455 | 2998 | ||||||||||||
| 08 | Johannesburg, AFS | 21949 | 13321 | 8834 | 4681 | 3016 | |||||||||||||||
| 09 | Barrow, AK | 21937 | 21928 | 17934 | 17919 | 11354 | 10093 | 10027 | 8936 | 8927 | 6646 | 5544 | 5538 | 5529 | 4687 | 4654 | 3497 | 3007 | 2992 | 2944 | |
| 11 | Albrook PAN | 21940 | 17901 | 10063 | 6589 | 5589 | 2902 | ||||||||||||||
| 13 | Santa Cruz, BOL | 21997 | 21988 | 21973 | 21946 | 17916 | 13315 | 11318 | 8957 | 6628 | 4660 | 3467 | 2983 | ||||||||
| 14 | Krasnoyarsk, RUS | 21990 | 17912 | 13321 | 10087 | 8886 | 6596 | 5622 | 4679 | 2905 | 2878 | ||||||||||
| 15 | Al Muharraq, BHR | 21982 | 17967 | 13354 | 11312 | 10075 | 8885 | 5544 | 2986 | ||||||||||||
| 16 | Agana, GUM | 17919 | 13312 | 11306 | 11288 | 8927 | 6652 | 5451 | |||||||||||||
| 17 | Telde, Gran Canaria, CNR | 21955 | 17928 | 13303 | 11348 | 8948 | 6529 | 5589 | 2905 |