US Forest Service - Sierra National Forest (CA)
From The RadioReference Wiki
| US Forests in California: | |||||
| Angeles | Inyo | Lassen | Modoc | Sequoia | Six Rivers |
| Cleveland | Klamath | Los Padres | Plumas | Shasta-Trinity | Stanislaus |
| Eldorado | Lake Tahoe BMU | Mendocino | San Bernardino | Sierra | Tahoe |
Contents
Sierra National Forest (SNF - Forest #15) "Sierra" KME 2-6
National Forests were called "Forest Reserves" when they were first established by Presidential Proclamation under the Forest Reserve Act of 1891. The U.S. Forest Service was established in 1905 and in 1907, the "Forest Reserves" were all renamed "National Forests." The Sierra Forest Reserve was established in 1893 and was 6 million acres in size. It covered lands that are now part of Yosemite National Park, Kings Canyon National Park: and the Stanislaus, Toiyabe, Inyo and Sequoia National Forests. The large size of this reserve was too large to manage and the "Sierra South Forest Reserve" was established in 1910, covering the land south of the Kings River. Other portions of this original forest reserve were eventually split up between the Sierra, Toiyabe, Inyo and Sequoia National Forests. The remaining National Forest land became the present Sierra National Forest. Located on the western slope of the central Sierra Nevada, it is known for its spectacular mountain scenery and abundant natural resources. The Sierra National Forest encompasses more than 1.3 million acres between 900 and 13,986 feet in elevation. The terrain includes rolling, oak-covered foothills, heavily forested middle elevation slopes and the starkly beautiful alpine landscape of the High Sierra. Abundant fish and wildlife, varied mountain flora and fauna and numerous recreational opportunities make the Sierra National Forest an outdoor lover's paradise. The Forest's many rugged wilderness areas makes it one of the most popular National Forests in the United States.
Approximately 383,000 acres of the forest are old growth, containing Lodgepole pine (Pinus contorta), Red fir (Abies magnifica), White fir (Abies concolor), Jeffrey pine (Pinus jeffreyi) and Ponderosa pine (Pinus ponderosa). The Sierra National Forest has two Giant Sequoia groves, the Nelder Grove and the McKinley Grove.
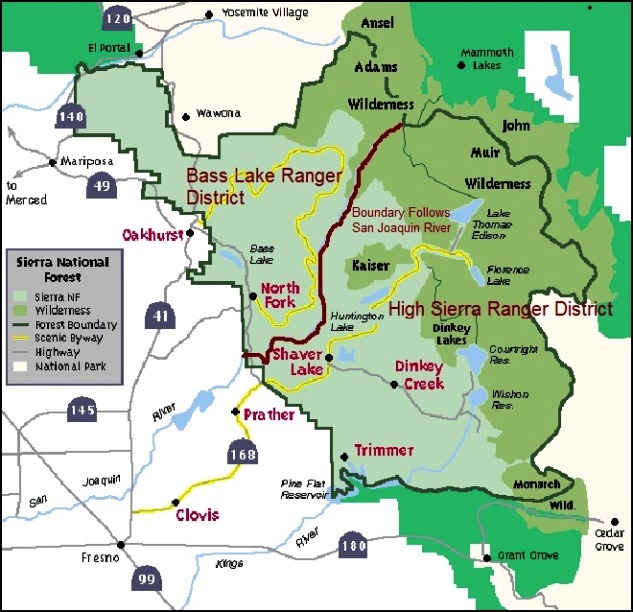
The Sierra National Forest is divided into the Bass Lake (District 1) (north of the San Joaquin River) and High Sierra (District 2) (south of the River) Ranger Districts. The Forest Supervisor's is in Clovis.
| Bass Lake Ranger District #1 | High Sierra Ranger District #3 |
|---|---|
| Mariposa Battalion #1 | Pine Ridge Battalion #3 |
| Station 11 - Jerseydale | Station 31 - Mountain Rest |
| Station 12 - Midpines | Station 32 - Big Creek |
| Station 13 - Batterson | |
| Station 14 Westfall | |
| Minarets Battalion #5 | Kings River Battalion #4 |
| Station 51 - North Fork | Station 41 - Trimmer |
| Station 52 - Clearwater | Station 42 - Blue Canyon |
| Station 53 - Minarets | Station 43 - Dinkey |
RADIO SYSTEM
The Sierra National Forest has an "Emergency Net" and an "Admin Net." The emergency net is used by fire management and law enforcement. The admin net is for all other functions. Channels have been provided to enable direct or simplex communications on each net. The installation of 5 of 11 of the NIFC command frequencies in the primary group of channel assignments is unusual. Another unusual feature of the forest's radio system is that the repeater input or access tone is not transmitted on the output frequency, instead a different set of tones is transmitted on the output. For example, the input tone for the Shuteye Peak repeater is Tone 5 - 146.2, but the tone transmitted on the output frequency is 82.5. The assignment of the output tones of the remaining repeaters has not been determined. They are all in the lower frequency range of CTCSS tones, such as 71.9 and 77.0. The linking system the forest uses is to be determined. The system's hub remote base is likely on Musick Mountain or Mt. Givens.
Other
The unit identifiers follow the function name, district, position number system. Common function names include resources, timber, recreation, wilderness, OHV (Off Highway Vehicle management) lands, special uses, range, wildlife, watershed, soils, fisheries, engineer, engineering, roads, O & M (Operations and Maintenance), ecology and possible additional. Not every forest uses all of these and some ID the same unit with a different name, example some forests call their O & M and roads units "engineering." A consolidation of the Mariposa Ranger District and the Minarets Ranger District into what is now called the "Bass Lake Ranger District"; and the consolidation of the Pineridge Ranger District and Kings River Ranger District into what is now called the "High Sierra Ranger District;" occurred in the late 1990s. Employees assigned to the Forest Supervisor's Office have identifiers beginning with the number 1. All ranger district non-fire personnel use the number 5 (Bass Lake Ranger District) or 3 (High Sierra Ranger District) following the function name.
San Luis National Refuge personnel identify in the 8100 series. Their two older engines are assigned number in the 3100 series (old Bakersfield BLM district numbers) and the 2 newer engines in the 8100 series. When the two older engines are replaced, they will receive the 8100 series numbers.
The Sierra National Forest Emergency Command Center provides service to the Sierra National Forest and the San Luis National Wildlife Refuge Complex located adjacent to the San Joaquin River in the Central Valley. The San Luis NWR Complex includes the San Luis National Wildlife Refuge (NWR), the Merced NWR, San Joaquin River NWR, and Grasslands Wildlife Management Area. The Complex office is in Los Banos. The Command Center is located at the Fresno Air Attack Base, an interagency Forest Service - Cal Fire facility at the Fresno Airport. The center is co located with Cal Fire's Fresno-Kings Unit Emergency Command Center. Each agency is included on the automatic initial attack dispatch plan of the other agency. The Forest Service dispatchers use the identifier "Sierra."
Channel Plan
| Channel | Tone(s) | Rx | Tx | Alpha Tag | Description |
| 1 | 171.4750 | 171.4750 | Adm/LE Dir | Sierra NF - Admin/Law Enforcement Net Direct | |
| 2 | 1-10 | 171.4750 | 163.6875 | Adm/LE Rpt | Sierra NF - Admin/Law Enforcement Net Repeater |
| 3 | 172.2250 | 172.2250 | Emer/Fire Dir | Sierra NF - Emergency/Fire Net Direct | |
| 4 | 1-10 | 172.2250 | 164.7875 | Emer/Fire Rpt | Sierra NF - Emergency/Fire Net Repeater |
| 5 | 168.6625 | 168.6625 | R5 Project | R5 Project | |
| 6 | 166.5500 | 166.5500 | R5 T4 | R5 Tac 4 | |
| 7 | 167.1125 | 167.1125 | R5 T5 | R5 Tac 5 | |
| 8 | 167.9625 | 167.9625 | R5 T7 | R5 Tac 7 | |
| 9 | 167.4750 | 167.4750 | A/G 41 CA3 P | National Air-Ground 41 CA Zone 3 Primary | |
| 10 | 168.6375 | 168.6375 | A/G 24 CA3 S | National Air-Ground 24 CA Zone 3 Secondary | |
| 11 | 1-16 | 168.7000 | 170.9750 | NIFC C1 Rpt | NIFC Command 1 Repeater (1) |
| 12 | 1-16 | 168.1000 | 170.4500 | NIFC C2 Rpt | NIFC Command 2 Repeater (1) |
| 13 | 1-16 | 168.0750 | 170.4250 | NIFC C3 Rpt | NIFC Command 3 Repeater (1) |
| 14 | 1-16 | 166.6125 | 168.4000 | NIFC C4 Rpt | NIFC Command 4 Repeater (1) |
| 15 | 1-16 | 167.1000 | 169.7500 | NIFC C5 Rpt | NIFC Command 5 Repeater (1) |
| 16 | 1 | 168.6250 | 168.6250 | Natl Air Grd | National Air Guard - Tone 1 Tx Side |
| 173.7625 | 164.8250 | SNF Serv | Service Net |
Revised 6-10-24
(1): The National Interagency Fire Center's Command repeaters are portable and installed when a fire or other large incident occurs. There aren't any permanently installed NIFC Command repeaters set up in locations on the Sierra National Forest or any other federal public lands. NIFC assigns a CTCSS tone for each incident to code guard each frequency to reduce the chances of one incident interfering with another distant incident. NIFC chooses any one of the 16 standard tones for incidents as required by the circumstances.
Tones
| Input Tone | Location - Nets repeaters equipped with | CTCSS Tone | Output Tone |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Mt. Bullion - Admin/Fire/Service | 110.9 | 74.4 |
| 2 | Signal Peak - Admin/Fire | 123.0 | 77.0 |
| 3 | Musick Mtn. - Admin/Fire/Service/Remote Base* | 131.8 | 79.7 |
| 4 | Patterson Mtn. - Admin/Fire/Service | 136.5 | 82.5 |
| 5 | Shuteye Peak - Admin/Fire | 146.2 | 85.4 |
| 6 | Black Mtn. - Admin/Fire | 156.7 | 88.5 |
| 7 | Mt. Tom - Admin/Fire | 167.9 | 91.5 |
| 8 | Delilah - Admin/Fire | 103.5 | 94.8 |
| 9 | Mt. Givens - Admin | 100.0 | TBD |
| 9 | Whitebark Vista- Fire/Service/Remote Base* | 100.0 | TBD |
| 10 | Fence Meadow - Admin/Fire | 127.3 | TBD |
| 11-16 | Not Assigned |
TBD = To Be Determined
The Sierra National Forest repeaters transmit a different and non-standard tone on the repeater output frequency. The tones for Mt. Givens, Whitebark Vista and Fence Meadows have yet to be determined. All output tones are believed to be in the lower CTCSS frequency range, i.e. 67.0 - 97.4. Good guesses for the remaining 3 repeaters would be 67.0, 71.9 and 97.4.
Remote Base*: These repeater sites also have microwave linked remote bases for the admin, fire and service nets and each remote base works the repeaters of all three nets regardless of location. There are three microwave base links not shown above as they are not on peaks or on peaks with VHF repeaters. These are at dispatch (Fresno Airport), Goat Mtn. and North Fork. The latter two provide microwave access for the North Fork Ranger Station, the headquarters of the Bass Lake Ranger District. Direct or simplex communications from field units with the dispatch and North Fork base stations is possible with the remote bases.
Related Links
- National Incident Radio Support Cache - These frequencies are used for large incidents, usually when a Type I or Type II Incident Management Team is assigned. This cache is used for fires, floods, tornadoes, hurricanes, visits of high ranking officials, such the U.S. President and the presidents of other countries, large law enforcement incidents, special events and other incidents where the federal government is utilizing the Incident Command System.
Return to DB page: United States Forest Service (CA)
| US Forests in California: | |||||
| Angeles | Inyo | Lassen | Modoc | Sequoia | Six Rivers |
| Cleveland | Klamath | Los Padres | Plumas | Shasta-Trinity | Stanislaus |
| Eldorado | Lake Tahoe BMU | Mendocino | San Bernardino | Sierra | Tahoe |
- California Fire Services
- California Fire Services Frequencies
- California Fire Services Aviation
- California Fire Services Aviation Frequencies
- California Law Enforcement
- California Law Enforcement Frequencies
- California Recreation or Attractions
- California Recreation or Attractions Frequencies
- US Forest Service in California
- US Forest Service Frequencies in California