Difference between revisions of "QDP2012/39"
From The RadioReference Wiki
< User:QDP2012
m (.) |
m (.) |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | (From: [[US Forest Service - | + | (From: [[US Forest Service - Modoc National Forest (CA)]] ) |
{{USFSinCA}} | {{USFSinCA}} | ||
| − | == ''' | + | == '''Modoc National Forest (MDF - Forest #09) "Modoc" KMB 700''' == |
| − | The | + | “The Smiles of Gods” is what the Native Americans, who first settled this land, called it. The forest is named for the county in which the greater part of the forest is situated. The county, in turn, is named after the Native American tribe, the Modocs. The history of the Modoc National Forest begins with the setting aside of two forest reserves by President Theodore Roosevelt in 1904 at the request of the local ranchers. A proclamation by Roosevelt on November 29, 1904 created the Warner Mountains Forest Reserve and the Modoc Forest Reserve, both renamed "National Forests" in 1907 when all Forest Reserves became National Forests. This same President added an additional 570,000 acres on February 13, 1908, and on July 2, 1908 combined the Warner Mountains and Modoc National Forests into one administrative unit, known thereafter as the Modoc National Forest. The forest covers 1,654,392 acres and is located on the on the huge Modoc Plateau where vegetation tends to be sparse. Recreation use is low as compared to the other 17 National Forests in California with approximately 175,000 visits. There are single developed recreation sites on other National Forests in California that have more visits. |
| − | The | + | Separated from the more heavily populated and intensively used areas of the Sacramento Valley by the main Sierra Nevada mountain ranges, the Modoc lies in the extreme northeast corner of California. The topography is diverse, ranging from the forested Warner Mountain range in the east, to the high plateaus dominated by sage steppe and ancient lava flows around Alturas, and culminating at the Medicine Highlands (the largest shield volcano in North America) in the west. The high desert climate in the valley areas consists of four distinct seasons and an average precipitation of 13 inches, a large part of which comes in the form of snow during the winter months of December to March. Elevation levels in the Modoc range from 9,906 feet at Eagle Peak in the South Warner Wilderness, to 4,000 feet in the valleys. |
| − | + | Some 43,400 acres of the forest have been identified as old growth, consisting primarily of Lodgepole pine (''Pinus contorta''), ponderosa pine (''Pinus ponderosa''), white fir (''Abies concolor''), red fir (''Abies magnifica'') and incense cedar (''Calocedrus decurrens''). | |
| − | The | + | The Modoc National Forest is divided into the Warner Mtn. (District 3), Big Valley (District 4), Devil's Garden (District 5) and Doublehead (District 6) Ranger Districts, with the Forest Supervisor's Office in Alturas. The Devil's Garden Ranger District is located in the Forest Supervisor's Office. |
| − | [[File: | + | [[File:USFS CA Modoc NF Small Map.png]] |
| − | |||
| Line 22: | Line 21: | ||
==='''RADIO SYSTEM'''=== | ==='''RADIO SYSTEM'''=== | ||
| − | The | + | The Modoc has a Forest Net, Admin Net and Service Net with only 6 repeater sites, the fewest of any National Forest in Region 5. The is a repeater for each net at each electronic site. The Modoc's gentle terrain is such that higher points, a few of which have electronic sites on them, sites can "see" a great deal of land. At least some of the sites are linked by microwave, but not much is known by hobbyists about the location of remote base stations and other design features of the system. |
==='''Other'''=== | ==='''Other'''=== | ||
| − | The Forest | + | The Modoc National Forest averages 103 wildland fires per year. The Lower Klamath Basin and Modoc National Wildlife Refuges average 8.6 fires per year. The Lava Beds National Monument averages 3.8 fires per year. |
| + | |||
| + | The unit identifier system for non-fire management is unknown. It is unknown what number the identifiers of non-fire employees of the Supervisor's Office are based on. The Modoc Interagency Communications Center coordinates and dispatches resources to respond to wildland fires and all risk incidents within the Modoc National Forest, Lava Beds National Monument and the Lower Klamath Basin and Modoc National Wildlife Refuges. Ranger District identifiers use the numbers 3, 4, 5 and 6. Lava Beds National Monument use the number 7 and the U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service uses the number 8. The identifier of the Communications Center is "Modoc." | ||
| Line 32: | Line 33: | ||
{| border="4" cellpadding="4" cellspacing="0" style="margin: 1em 1em 1em 0; background: #f9f9f9; border: 2px #777777 solid; border-collapse: collapse;" class="wikitable sortable" | {| border="4" cellpadding="4" cellspacing="0" style="margin: 1em 1em 1em 0; background: #f9f9f9; border: 2px #777777 solid; border-collapse: collapse;" class="wikitable sortable" | ||
| − | |+ style="font-size: larger" | ''' | + | |+ style="font-size: larger" | '''Modoc National Forest Channel Lineup''' |
|'''Channel '''||'''Tone(s) '''||'''Rx '''||'''Tx '''||'''Alpha Tag '''||'''Description ''' | |'''Channel '''||'''Tone(s) '''||'''Rx '''||'''Tx '''||'''Alpha Tag '''||'''Description ''' | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | |1|||| | + | |1||1||168.7500||168.7500||MDF1 FrstNet Dir||Modoc NF Forest Net Direct |
| + | |- | ||
| + | |2||1-8||168.7500||170.1750||MDF2 FrstNet Rpt||Modoc NF Forest Net Repeater | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | | + | |3||1||173.7875||173.7875||MDF3 Adm Dir||Modoc NF Admin Net Direct |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | | + | |4||1-8||173.7875||162.4875||MDF4 Adm Rpt||Modoc NF Admin Net Repeater |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | | + | |5||1-8||164.1000||164.8000||MDF5 Serv Rpt||Modoc NF Service Net Repeater |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | | + | |6||||168.0500||168.0500||MDF6 NIFC T1||NIFC Tac 1 |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | | + | |7||||168.2000||168.2000||MDF7 NIFC T2||NIFC Tac 2 |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | | + | |8||||168.6000||168.6000||MDF8 NIFC T3||NIFC Tac 3 |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | | + | |9||||167.6000||167.6000||MDF9 AG43 P||National Air to Ground 43 CA Zone 01 Primary |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | | + | |10||||168.6625||168.6625||MDF10 R5 Proj||Region 5 Project/Fire Net |
| − | + | |- | |
| − | + | |11||4||171.6250||171.6250||MDF11 NODFireD||BLM Northern California District Fire Net Direct | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | | | ||
| − | | | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | | + | |12||1-8||171.6250||164.2500||MDF12 NODFireR||BLM Northern California District Fire Net Repeater |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | | + | |13||||151.2500||151.2500||MDF13 LMU Dir||Cal Fire Lassen-Modoc-Plumas Local Direct |
|- | |- | ||
| + | |14||xx||151.2500||159.405||MDF14 LMU Rpt||Cal Fire Lassen-Modoc-Plumas Local Repeater | ||
|} | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | On Channels 1 & 3 Tone 1 (110.9) must be used to contact dispatch or a Ranger District office. | ||
==='''Tones'''=== | ==='''Tones'''=== | ||
| Line 73: | Line 73: | ||
{| border="4" cellpadding="4" cellspacing="0" style="margin: 1em 1em 1em 0; background: #f9f9f9; border: 2px #777777 solid; border-collapse: collapse; float;" | {| border="4" cellpadding="4" cellspacing="0" style="margin: 1em 1em 1em 0; background: #f9f9f9; border: 2px #777777 solid; border-collapse: collapse; float;" | ||
| − | |+ style="font-size: larger; font-weight: bold;" | | + | |+ style="font-size: larger; font-weight: bold;" |MDF Repeaters |
!Tone | !Tone | ||
!Location | !Location | ||
!CTCSS Tone | !CTCSS Tone | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | |1|| | + | |1||Channels 1&3||110.9 |
|- | |- | ||
| − | |2|| | + | |2||Sugar Hill||123.0 |
|- | |- | ||
| − | |3|| | + | |3||Likely Mtn.||131.8 |
|- | |- | ||
| − | |4|| | + | |4||49 Mtn.||136.5 |
|- | |- | ||
| − | |5|| | + | |5||Grouse Mtn.||146.2 |
|- | |- | ||
| − | |6|| | + | |6||Fire Repeater||156.7 |
|- | |- | ||
| − | |7|| | + | |7||Red Shale Butte||167.9 |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
|- | |- | ||
| + | |8||Widow Mtn.||103.5 | ||
|} | |} | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
===Related Links=== | ===Related Links=== | ||
Revision as of 19:22, 29 June 2016
(From: US Forest Service - Modoc National Forest (CA) )
| US Forests in California: | |||||
| Angeles | Inyo | Lassen | Modoc | Sequoia | Six Rivers |
| Cleveland | Klamath | Los Padres | Plumas | Shasta-Trinity | Stanislaus |
| Eldorado | Lake Tahoe BMU | Mendocino | San Bernardino | Sierra | Tahoe |
Contents
Modoc National Forest (MDF - Forest #09) "Modoc" KMB 700
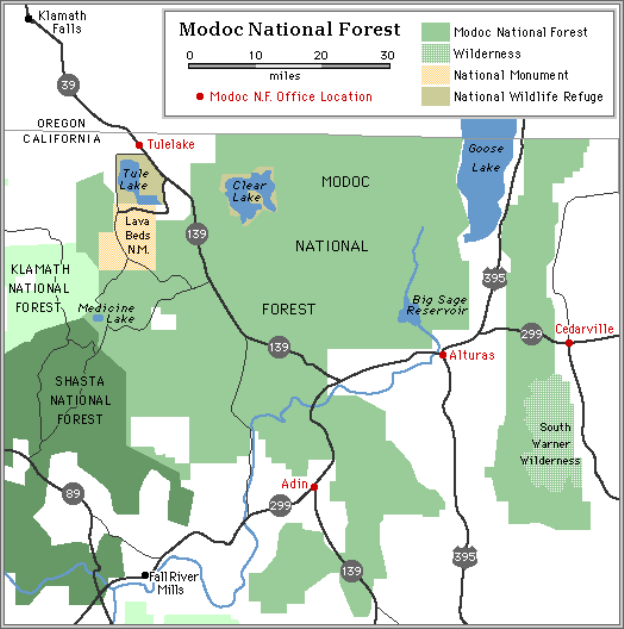
“The Smiles of Gods” is what the Native Americans, who first settled this land, called it. The forest is named for the county in which the greater part of the forest is situated. The county, in turn, is named after the Native American tribe, the Modocs. The history of the Modoc National Forest begins with the setting aside of two forest reserves by President Theodore Roosevelt in 1904 at the request of the local ranchers. A proclamation by Roosevelt on November 29, 1904 created the Warner Mountains Forest Reserve and the Modoc Forest Reserve, both renamed "National Forests" in 1907 when all Forest Reserves became National Forests. This same President added an additional 570,000 acres on February 13, 1908, and on July 2, 1908 combined the Warner Mountains and Modoc National Forests into one administrative unit, known thereafter as the Modoc National Forest. The forest covers 1,654,392 acres and is located on the on the huge Modoc Plateau where vegetation tends to be sparse. Recreation use is low as compared to the other 17 National Forests in California with approximately 175,000 visits. There are single developed recreation sites on other National Forests in California that have more visits.
Separated from the more heavily populated and intensively used areas of the Sacramento Valley by the main Sierra Nevada mountain ranges, the Modoc lies in the extreme northeast corner of California. The topography is diverse, ranging from the forested Warner Mountain range in the east, to the high plateaus dominated by sage steppe and ancient lava flows around Alturas, and culminating at the Medicine Highlands (the largest shield volcano in North America) in the west. The high desert climate in the valley areas consists of four distinct seasons and an average precipitation of 13 inches, a large part of which comes in the form of snow during the winter months of December to March. Elevation levels in the Modoc range from 9,906 feet at Eagle Peak in the South Warner Wilderness, to 4,000 feet in the valleys.
Some 43,400 acres of the forest have been identified as old growth, consisting primarily of Lodgepole pine (Pinus contorta), ponderosa pine (Pinus ponderosa), white fir (Abies concolor), red fir (Abies magnifica) and incense cedar (Calocedrus decurrens).
The Modoc National Forest is divided into the Warner Mtn. (District 3), Big Valley (District 4), Devil's Garden (District 5) and Doublehead (District 6) Ranger Districts, with the Forest Supervisor's Office in Alturas. The Devil's Garden Ranger District is located in the Forest Supervisor's Office.
RADIO SYSTEM
The Modoc has a Forest Net, Admin Net and Service Net with only 6 repeater sites, the fewest of any National Forest in Region 5. The is a repeater for each net at each electronic site. The Modoc's gentle terrain is such that higher points, a few of which have electronic sites on them, sites can "see" a great deal of land. At least some of the sites are linked by microwave, but not much is known by hobbyists about the location of remote base stations and other design features of the system.
Other
The Modoc National Forest averages 103 wildland fires per year. The Lower Klamath Basin and Modoc National Wildlife Refuges average 8.6 fires per year. The Lava Beds National Monument averages 3.8 fires per year.
The unit identifier system for non-fire management is unknown. It is unknown what number the identifiers of non-fire employees of the Supervisor's Office are based on. The Modoc Interagency Communications Center coordinates and dispatches resources to respond to wildland fires and all risk incidents within the Modoc National Forest, Lava Beds National Monument and the Lower Klamath Basin and Modoc National Wildlife Refuges. Ranger District identifiers use the numbers 3, 4, 5 and 6. Lava Beds National Monument use the number 7 and the U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service uses the number 8. The identifier of the Communications Center is "Modoc."
Channel Plan
| Channel | Tone(s) | Rx | Tx | Alpha Tag | Description |
| 1 | 1 | 168.7500 | 168.7500 | MDF1 FrstNet Dir | Modoc NF Forest Net Direct |
| 2 | 1-8 | 168.7500 | 170.1750 | MDF2 FrstNet Rpt | Modoc NF Forest Net Repeater |
| 3 | 1 | 173.7875 | 173.7875 | MDF3 Adm Dir | Modoc NF Admin Net Direct |
| 4 | 1-8 | 173.7875 | 162.4875 | MDF4 Adm Rpt | Modoc NF Admin Net Repeater |
| 5 | 1-8 | 164.1000 | 164.8000 | MDF5 Serv Rpt | Modoc NF Service Net Repeater |
| 6 | 168.0500 | 168.0500 | MDF6 NIFC T1 | NIFC Tac 1 | |
| 7 | 168.2000 | 168.2000 | MDF7 NIFC T2 | NIFC Tac 2 | |
| 8 | 168.6000 | 168.6000 | MDF8 NIFC T3 | NIFC Tac 3 | |
| 9 | 167.6000 | 167.6000 | MDF9 AG43 P | National Air to Ground 43 CA Zone 01 Primary | |
| 10 | 168.6625 | 168.6625 | MDF10 R5 Proj | Region 5 Project/Fire Net | |
| 11 | 4 | 171.6250 | 171.6250 | MDF11 NODFireD | BLM Northern California District Fire Net Direct |
| 12 | 1-8 | 171.6250 | 164.2500 | MDF12 NODFireR | BLM Northern California District Fire Net Repeater |
| 13 | 151.2500 | 151.2500 | MDF13 LMU Dir | Cal Fire Lassen-Modoc-Plumas Local Direct | |
| 14 | xx | 151.2500 | 159.405 | MDF14 LMU Rpt | Cal Fire Lassen-Modoc-Plumas Local Repeater |
On Channels 1 & 3 Tone 1 (110.9) must be used to contact dispatch or a Ranger District office.
Tones
Information about the tones transmitted on the output frequency is unavailable.
| Tone | Location | CTCSS Tone |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Channels 1&3 | 110.9 |
| 2 | Sugar Hill | 123.0 |
| 3 | Likely Mtn. | 131.8 |
| 4 | 49 Mtn. | 136.5 |
| 5 | Grouse Mtn. | 146.2 |
| 6 | Fire Repeater | 156.7 |
| 7 | Red Shale Butte | 167.9 |
| 8 | Widow Mtn. | 103.5 |
Related Links
- National Incident Radio Support Cache - These frequencies are used for large incidents, usually when a Type I or Type II Incident Management Team is assigned. This cache is used for fires, floods, tornadoes, hurricanes, visits of high ranking officials, such the U.S. President and the presidents of other countries, large law enforcement incidents, special events and other incidents where the federal government is utilizing the Incident Command System.
Return to DB page: United States Forest Service (CA)
| US Forests in California: | |||||
| Angeles | Inyo | Lassen | Modoc | Sequoia | Six Rivers |
| Cleveland | Klamath | Los Padres | Plumas | Shasta-Trinity | Stanislaus |
| Eldorado | Lake Tahoe BMU | Mendocino | San Bernardino | Sierra | Tahoe |