Difference between revisions of "QDP2012/39"
From The RadioReference Wiki
< User:QDP2012
m (.) |
m (.) |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | (From: [[US Forest Service - | + | (From: [[US Forest Service - Inyo National Forest (CA)]] ) |
{{USFSinCA}} | {{USFSinCA}} | ||
| − | == ''' | + | ==''' Inyo National Forest (INF - Forest #04) "Inyo" KMB 6-7-0''' == |
| + | Established by proclamation on May 25, 1907 by President Teddy Roosevelt covering 221,324 acres along the river along the Owens River. First established to secure the water interests of the City of Los Angeles, the Inyo National Forest has been expanded and contracted at least four times since its creation. Most of the original lands designated as the Inyo National Forest are no longer part of the Forest and are now owned by the Los Angeles Department of Water and Power. These lands were later returned to the public domain and portions of the Sierra National Forest, east of the Sierra crest as well as the White-Inyo Mountains, were designated as the Inyo National Forest. The forest now covers 2 million acres. The Inyo National Forest extends 165 miles from Conway Summit in the north and to the Kern Plateau in the south. The Inyo has over 10,500 feet of elevation difference, from 3,900 feet near Owens Lake to 14,494 on the peak of Mt. Whitney, highest peak in the continental United States. | ||
| − | + | The Forest includes the Mono Lake National Forest Scenic Area, Boundary Peak - the highest peak in the State of Nevada at 13,140 feet, the world's largest Jeffrey Pine Forest located east of Mammoth Lakes and south of Mono Lake, 2 Wild & Scenic Rivers, 5 Visitor Centers, 3 Scenic Byways, 2 Alpine Ski Areas and 1 Nordic Ski Center. The world's oldest tree, Methuselah, is a 4700 year old Bristlecone Pine growing in the Ancient Bristlecone Pine Forest atop the White Mountains. The Inyo has 9 Congressionally designated Wilderness Areas covering more than 800,000 acres. Among them is the John Muir Wilderness, which receives the most visitor use per acre, per year, of any wilderness area in the western United States. The Mt. Whitney trail corridor is the most challenging trail to manage in the National Forest System and has the only day use quota and permit requirement on any National Forest. This land, where the desert meets the mountains, was first reserved for its timber, water and forage. Thanks to decades of public management, the lands of the Inyo National Forest continue to supply clean water to over 3.8 million people, renewable forests, homes for wildlife from Sierra Nevada bighorn sheep to the Golden Trout, and the peace of the outdoors for nearly four million people annually, the most for a National Forest in California.. The Inyo consistently ranks in the top 5 National Forests in the U.S. in recreation use and its developed recreation sites (campgrounds, picnic areas, nature trails interpretive and historical sites, visitor centers, etc) receive the most use of any one National Forest in the country, approximately twice that of the #2 National Forest in this category. | |
| − | + | There are 238,000 acres of old-growth forest on the Inyo National Forest, primarily consisting of Lodgepole pine (''Pinus contorta'') and Jeffrey pine (''Pinus jeffreyi''). | |
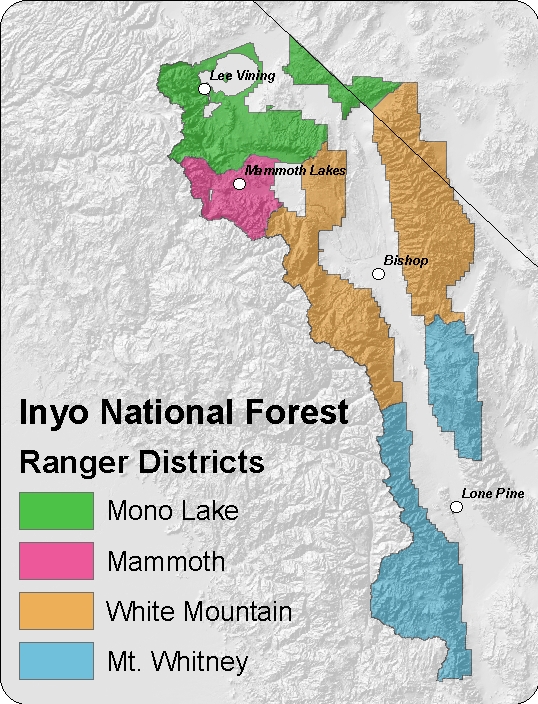
| − | + | The forest is divided into the Mono Lake (District 1), Mammoth (District 2), White Mountain (District 3) and Mt. Whitney (District 4) Ranger Districts with the Forest Supervisor's Office in Bishop. | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | [[File:R5 2014 Inyo NF RD Map.jpg]] | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | File:R5 | ||
| − | |||
==='''RADIO SYSTEM'''=== | ==='''RADIO SYSTEM'''=== | ||
| − | The | + | The Inyo National Forest has 3 nets, Forest Net - North, Forest Net - South and Service Net. The Mono Lake and Mammoth Ranger Districts are on the North Net. The White Mountain Ranger District uses the North Net for those areas north of the bottom of the Sherwin Grade on U.S. 395 (McGee and Rock Creek Canyons and the Casa Diablo area east of Crowley Lake) and the South Net south of that point (Buttermilk Country, Bishop Creek and Big Pine Creek to Division Creek as well as the White Mountains (Westguard Pass north). The Mt. Whitney District uses the South Net only (from Division Creek south to the Kern Plateau and the Inyo Mountains - south of Westguard Pass). Some areas of Bishop Creek and the north end of the White Mountains are covered by Glass Mountain only (Tone 3) and are exceptions to this North Net/South Net configuration. Silver Peak, northeast of Bishop in the White Mountains is the only electronic site with repeaters on all 3 nets and is the location of the North Net remote base. The South Net remote base is on Mazourka Peak northeast of Independence. The links for the remote bases utilize UHF only. The Inyo National Forest does not have direct, or simplex channels provided for its 3 Nets. |
| − | + | ==='''Other'''=== | |
| − | + | The Inyo National Forest fire organization is combined with the Bureau of Land Management (BLM) Bishop Field Office fire organization into one Interagency Fire Management Organization. The management area combines the public land of the Inyo National Forest and Bishop Field Office in Inyo and Mono Counties in California and part of Mineral and Esmeralda Counties in Nevada, covering over 2 million acres. The Interagency Fire Management Organization maintains 8 fire stations with 9 engines, 7 fire prevention patrol units, 2 water tenders, a 10-person fire use management hand crew, a 20-person hotshot crew, an air tanker reload base and a helitack base. This organization, as well as the non-fire management personnel of both agencies, use the two Inyo National Forest nets for its primary nets. The BLM net is used as an alternate dispatch or command net when multiple fire starts/large incidents occur. | |
| − | + | In Mono County the wildland fire State Responsibility Area (SRA) inside the Inyo National Forest is in the direct protection area of the Inyo National Forest. This is provided under contract and the state pays the USFS for this service. The SRA outside the National Forest boundaries in Mono County is in the direct protection area of the BLM. In exchange the BLM land in Inyo County is in the direct protection area of Cal Fire's San Bernardino Unit, Owens Valley Division. | |
| + | The unit identifiers follow the '''function name''', district number, position number system. Employees working in or out of the Supervisor's Office use identifiers have a "5" following the function name. The Owens Valley Interagency Dispatch Center is located in the joint Inyo National Forest-BLM Bishop Field Office facility in Bishop. It also provides dispatch for the BLM Central California District - Bishop Field Office. This center provides dispatching for two National Park Service units: Devils Postpile National Monument and the Manzanar National Historic Site. Law enforcement dispatching for Devils Postpile is provided by Yosemite National Park using a link to its law enforcement net located on Mammoth Mountain. This center is not a 24 hour operation, but is open 7 days per week, year long. When the Owens Valley Center is shut down the San Bernardino Federal Interagency Communications Center ("San Bernardino") provides dispatching as it is able to control the entire Inyo/BLM radio system. The center's identifier is "Inyo." | ||
| − | ==='''Channel Plan''' === | + | ==='''Channel Plan'''=== |
{| border="4" cellpadding="4" cellspacing="0" style="margin: 1em 1em 1em 0; background: #f9f9f9; border: 2px #777777 solid; border-collapse: collapse;" class="wikitable sortable" | {| border="4" cellpadding="4" cellspacing="0" style="margin: 1em 1em 1em 0; background: #f9f9f9; border: 2px #777777 solid; border-collapse: collapse;" class="wikitable sortable" | ||
| − | |+ style="font-size: larger" | ''' | + | |+ style="font-size: larger" | '''Inyo National Forest Channel Lineup''' |
|'''Channel '''||'''Tone(s) '''||'''Rx '''||'''Tx '''||'''Alpha Tag '''||'''Description ''' | |'''Channel '''||'''Tone(s) '''||'''Rx '''||'''Tx '''||'''Alpha Tag '''||'''Description ''' | ||
|- | |- | ||
| + | |1||1-3, 8-9, 10||168.1250||173.8000||INF1 Frst N||North Forest Repeater Net | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | | + | |2||||168.2000||168.2000||INF2 NIFC T2||NIFC Tac 2 |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | | + | |3||4-8||168.7250||173.8375||INF3 Frst S||South Forest Repeater Net |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | | + | |4||3-4, 8||172.4000||164.1250||INF4 Serv||Service Repeater Net |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | | + | |5||||167.4750||167.4750||INF5 A/G41 CA3 P||National Air to Ground 41 - California Zone 3 Primary |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | | + | |6||||168.6625||168.6625||INF6 R5 Proj||Region 5 Project/Fire Net |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | | + | |7||4, 5, 8, 10||169.7125||163.1250||INF7 BLM Bshp FO||BLM Bishop Field Office Net |
|- | |- | ||
| − | |** | + | |*||||173.7325||173.7625||INF BC Tac||Inyo NF Backcountry Tactical |
| + | |||
| + | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | *Inyo National Forest Radio Group 7 - North Backcountry, Channel 9. May be used for backcountry extenders (as well as backcountry repeaters, but this is unknown). Channel is labeled "Trails." | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==='''Channel Plan Upcoming Changes'''=== | ||
| + | |||
| + | {| border="4" cellpadding="4" cellspacing="0" style="margin: 1em 1em 1em 0; background: #f9f9f9; border: 2px #777777 solid; border-collapse: collapse;" class="wikitable sortable" | ||
| + | |+ style="font-size: larger" | '''Inyo National Forest Channel Lineup''' | ||
| + | |'''Channel '''||'''Tone(s) '''||'''Rx '''||'''Tx '''||'''Alpha Tag '''||'''Description ''' | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | | + | |1||1-3, 8-9, 10||173.8000||165.0125||INF1 Frst N||North Forest Repeater Net (Changing 2017) |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | | + | |3||4-8||173.8375||166.2625||INF3 Frst S||South Forest Repeater Net (Changing Late Summer 2016) |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | | + | |4||3-4, 8||172.4000||164.1250||INF4 Serv||Service Repeater Net (Change Completed Fall 2015) |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | | + | |
| − | |- | + | |} |
| − | | | + | |
| + | ==='''Tones'''=== | ||
| + | |||
| + | All repeaters transmit the input tone on the output frequency. | ||
| + | |||
| + | {| border="4" cellpadding="4" cellspacing="0" style="margin: 1em 1em 1em 0; background: #f9f9f9; border: 2px #777777 solid; border-collapse: collapse; float;" | ||
| + | |+ style="font-size: larger; font-weight: bold;" |INF North Forest Net Tones | ||
| + | !Tone | ||
| + | !Location | ||
| + | !CTCSS Tone | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | | + | |1||Mt. Warren||110.9 |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | | + | |2||Mammoth Mtn.||123.0 |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | | + | |3||Glass Mtn.||131.8 |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | | + | |8||Silver Peak||103.5 |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | | + | |9||June Mtn.||100.0 |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
|- | |- | ||
| + | |10||Sweetwater*||107.2 | ||
|} | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | *Located on the Toiyabe NF near the U.S. 395/California State Route 108 junction. It provides radio coverage for the northern portion of the Bishop Field Office jurisdiction. | ||
| − | |||
| − | {| border="4" cellpadding="4" cellspacing="0" style="margin: 1em 1em 1em 0; background: #f9f9f9; border: 2px #777777 solid; border-collapse: collapse; | + | {| border="4" cellpadding="4" cellspacing="0" style="margin: 1em 1em 1em 0; background: #f9f9f9; border: 2px #777777 solid; border-collapse: collapse; float;" |
| − | |+ style="font-size: larger" | | + | |+ style="font-size: larger; font-weight: bold;" |INF South Forest Net Tones |
| − | + | !Tone | |
| + | !Location | ||
| + | !CTCSS Tone | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |4||Mazourka Peak||136.5 | ||
|- | |- | ||
| + | |5||Cerro Gordo Peak||146.2 | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | | + | |6||Olancha Peak||156.7 |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | | + | |7||Piper Peak||167.9 |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | | + | |8||Silver Peak||103.5 |
|- | |- | ||
| + | |||
|} | |} | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
{| border="4" cellpadding="4" cellspacing="0" style="margin: 1em 1em 1em 0; background: #f9f9f9; border: 2px #777777 solid; border-collapse: collapse; float;" | {| border="4" cellpadding="4" cellspacing="0" style="margin: 1em 1em 1em 0; background: #f9f9f9; border: 2px #777777 solid; border-collapse: collapse; float;" | ||
| − | |+ style="font-size: larger; font-weight: bold;" | | + | |+ style="font-size: larger; font-weight: bold;" |INF Service Net Tones |
!Tone | !Tone | ||
!Location | !Location | ||
!CTCSS Tone | !CTCSS Tone | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | | + | |3||Glass Mtn.||131.8 |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | | + | |4||Mazourka Peak||136.5 |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | | + | |8||Silver Peak||103.5 |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | | + | |
| − | |- | + | |} |
| − | | | + | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | {| border="4" cellpadding="4" cellspacing="0" style="margin: 1em 1em 1em 0; background: #f9f9f9; border: 2px #777777 solid; border-collapse: collapse; float;" | |
| + | |+ style="font-size: larger; font-weight: bold;" |BLM Bishop Field Office Net Tones | ||
| + | !Tone | ||
| + | !Location | ||
| + | !CTCSS Tone | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | | + | |4||Potato Peak||136.5 |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | | + | |5||Cerro Gordo Peak||146.2 |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | | + | |8||Silver Peak||103.5 |
|- | |- | ||
| − | |10|| | + | |10||Sweetwater||107.2 |
|- | |- | ||
| − | |||
|} | |} | ||
Revision as of 19:19, 29 June 2016
(From: US Forest Service - Inyo National Forest (CA) )
| US Forests in California: | |||||
| Angeles | Inyo | Lassen | Modoc | Sequoia | Six Rivers |
| Cleveland | Klamath | Los Padres | Plumas | Shasta-Trinity | Stanislaus |
| Eldorado | Lake Tahoe BMU | Mendocino | San Bernardino | Sierra | Tahoe |
Contents
Inyo National Forest (INF - Forest #04) "Inyo" KMB 6-7-0
Established by proclamation on May 25, 1907 by President Teddy Roosevelt covering 221,324 acres along the river along the Owens River. First established to secure the water interests of the City of Los Angeles, the Inyo National Forest has been expanded and contracted at least four times since its creation. Most of the original lands designated as the Inyo National Forest are no longer part of the Forest and are now owned by the Los Angeles Department of Water and Power. These lands were later returned to the public domain and portions of the Sierra National Forest, east of the Sierra crest as well as the White-Inyo Mountains, were designated as the Inyo National Forest. The forest now covers 2 million acres. The Inyo National Forest extends 165 miles from Conway Summit in the north and to the Kern Plateau in the south. The Inyo has over 10,500 feet of elevation difference, from 3,900 feet near Owens Lake to 14,494 on the peak of Mt. Whitney, highest peak in the continental United States.
The Forest includes the Mono Lake National Forest Scenic Area, Boundary Peak - the highest peak in the State of Nevada at 13,140 feet, the world's largest Jeffrey Pine Forest located east of Mammoth Lakes and south of Mono Lake, 2 Wild & Scenic Rivers, 5 Visitor Centers, 3 Scenic Byways, 2 Alpine Ski Areas and 1 Nordic Ski Center. The world's oldest tree, Methuselah, is a 4700 year old Bristlecone Pine growing in the Ancient Bristlecone Pine Forest atop the White Mountains. The Inyo has 9 Congressionally designated Wilderness Areas covering more than 800,000 acres. Among them is the John Muir Wilderness, which receives the most visitor use per acre, per year, of any wilderness area in the western United States. The Mt. Whitney trail corridor is the most challenging trail to manage in the National Forest System and has the only day use quota and permit requirement on any National Forest. This land, where the desert meets the mountains, was first reserved for its timber, water and forage. Thanks to decades of public management, the lands of the Inyo National Forest continue to supply clean water to over 3.8 million people, renewable forests, homes for wildlife from Sierra Nevada bighorn sheep to the Golden Trout, and the peace of the outdoors for nearly four million people annually, the most for a National Forest in California.. The Inyo consistently ranks in the top 5 National Forests in the U.S. in recreation use and its developed recreation sites (campgrounds, picnic areas, nature trails interpretive and historical sites, visitor centers, etc) receive the most use of any one National Forest in the country, approximately twice that of the #2 National Forest in this category.
There are 238,000 acres of old-growth forest on the Inyo National Forest, primarily consisting of Lodgepole pine (Pinus contorta) and Jeffrey pine (Pinus jeffreyi).
The forest is divided into the Mono Lake (District 1), Mammoth (District 2), White Mountain (District 3) and Mt. Whitney (District 4) Ranger Districts with the Forest Supervisor's Office in Bishop.
RADIO SYSTEM
The Inyo National Forest has 3 nets, Forest Net - North, Forest Net - South and Service Net. The Mono Lake and Mammoth Ranger Districts are on the North Net. The White Mountain Ranger District uses the North Net for those areas north of the bottom of the Sherwin Grade on U.S. 395 (McGee and Rock Creek Canyons and the Casa Diablo area east of Crowley Lake) and the South Net south of that point (Buttermilk Country, Bishop Creek and Big Pine Creek to Division Creek as well as the White Mountains (Westguard Pass north). The Mt. Whitney District uses the South Net only (from Division Creek south to the Kern Plateau and the Inyo Mountains - south of Westguard Pass). Some areas of Bishop Creek and the north end of the White Mountains are covered by Glass Mountain only (Tone 3) and are exceptions to this North Net/South Net configuration. Silver Peak, northeast of Bishop in the White Mountains is the only electronic site with repeaters on all 3 nets and is the location of the North Net remote base. The South Net remote base is on Mazourka Peak northeast of Independence. The links for the remote bases utilize UHF only. The Inyo National Forest does not have direct, or simplex channels provided for its 3 Nets.
Other
The Inyo National Forest fire organization is combined with the Bureau of Land Management (BLM) Bishop Field Office fire organization into one Interagency Fire Management Organization. The management area combines the public land of the Inyo National Forest and Bishop Field Office in Inyo and Mono Counties in California and part of Mineral and Esmeralda Counties in Nevada, covering over 2 million acres. The Interagency Fire Management Organization maintains 8 fire stations with 9 engines, 7 fire prevention patrol units, 2 water tenders, a 10-person fire use management hand crew, a 20-person hotshot crew, an air tanker reload base and a helitack base. This organization, as well as the non-fire management personnel of both agencies, use the two Inyo National Forest nets for its primary nets. The BLM net is used as an alternate dispatch or command net when multiple fire starts/large incidents occur.
In Mono County the wildland fire State Responsibility Area (SRA) inside the Inyo National Forest is in the direct protection area of the Inyo National Forest. This is provided under contract and the state pays the USFS for this service. The SRA outside the National Forest boundaries in Mono County is in the direct protection area of the BLM. In exchange the BLM land in Inyo County is in the direct protection area of Cal Fire's San Bernardino Unit, Owens Valley Division.
The unit identifiers follow the function name, district number, position number system. Employees working in or out of the Supervisor's Office use identifiers have a "5" following the function name. The Owens Valley Interagency Dispatch Center is located in the joint Inyo National Forest-BLM Bishop Field Office facility in Bishop. It also provides dispatch for the BLM Central California District - Bishop Field Office. This center provides dispatching for two National Park Service units: Devils Postpile National Monument and the Manzanar National Historic Site. Law enforcement dispatching for Devils Postpile is provided by Yosemite National Park using a link to its law enforcement net located on Mammoth Mountain. This center is not a 24 hour operation, but is open 7 days per week, year long. When the Owens Valley Center is shut down the San Bernardino Federal Interagency Communications Center ("San Bernardino") provides dispatching as it is able to control the entire Inyo/BLM radio system. The center's identifier is "Inyo."
Channel Plan
| Channel | Tone(s) | Rx | Tx | Alpha Tag | Description |
| 1 | 1-3, 8-9, 10 | 168.1250 | 173.8000 | INF1 Frst N | North Forest Repeater Net |
| 2 | 168.2000 | 168.2000 | INF2 NIFC T2 | NIFC Tac 2 | |
| 3 | 4-8 | 168.7250 | 173.8375 | INF3 Frst S | South Forest Repeater Net |
| 4 | 3-4, 8 | 172.4000 | 164.1250 | INF4 Serv | Service Repeater Net |
| 5 | 167.4750 | 167.4750 | INF5 A/G41 CA3 P | National Air to Ground 41 - California Zone 3 Primary | |
| 6 | 168.6625 | 168.6625 | INF6 R5 Proj | Region 5 Project/Fire Net | |
| 7 | 4, 5, 8, 10 | 169.7125 | 163.1250 | INF7 BLM Bshp FO | BLM Bishop Field Office Net |
| * | 173.7325 | 173.7625 | INF BC Tac | Inyo NF Backcountry Tactical |
- Inyo National Forest Radio Group 7 - North Backcountry, Channel 9. May be used for backcountry extenders (as well as backcountry repeaters, but this is unknown). Channel is labeled "Trails."
Channel Plan Upcoming Changes
| Channel | Tone(s) | Rx | Tx | Alpha Tag | Description |
| 1 | 1-3, 8-9, 10 | 173.8000 | 165.0125 | INF1 Frst N | North Forest Repeater Net (Changing 2017) |
| 3 | 4-8 | 173.8375 | 166.2625 | INF3 Frst S | South Forest Repeater Net (Changing Late Summer 2016) |
| 4 | 3-4, 8 | 172.4000 | 164.1250 | INF4 Serv | Service Repeater Net (Change Completed Fall 2015) |
Tones
All repeaters transmit the input tone on the output frequency.
| Tone | Location | CTCSS Tone |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Mt. Warren | 110.9 |
| 2 | Mammoth Mtn. | 123.0 |
| 3 | Glass Mtn. | 131.8 |
| 8 | Silver Peak | 103.5 |
| 9 | June Mtn. | 100.0 |
| 10 | Sweetwater* | 107.2 |
- Located on the Toiyabe NF near the U.S. 395/California State Route 108 junction. It provides radio coverage for the northern portion of the Bishop Field Office jurisdiction.
| Tone | Location | CTCSS Tone |
|---|---|---|
| 4 | Mazourka Peak | 136.5 |
| 5 | Cerro Gordo Peak | 146.2 |
| 6 | Olancha Peak | 156.7 |
| 7 | Piper Peak | 167.9 |
| 8 | Silver Peak | 103.5 |
| Tone | Location | CTCSS Tone |
|---|---|---|
| 3 | Glass Mtn. | 131.8 |
| 4 | Mazourka Peak | 136.5 |
| 8 | Silver Peak | 103.5 |
| Tone | Location | CTCSS Tone |
|---|---|---|
| 4 | Potato Peak | 136.5 |
| 5 | Cerro Gordo Peak | 146.2 |
| 8 | Silver Peak | 103.5 |
| 10 | Sweetwater | 107.2 |
Related Links
- National Incident Radio Support Cache - These frequencies are used for large incidents, usually when a Type I or Type II Incident Management Team is assigned. This cache is used for fires, floods, tornadoes, hurricanes, visits of high ranking officials, such the U.S. President and the presidents of other countries, large law enforcement incidents, special events and other incidents where the federal government is utilizing the Incident Command System.
Return to DB page: United States Forest Service (CA)
| US Forests in California: | |||||
| Angeles | Inyo | Lassen | Modoc | Sequoia | Six Rivers |
| Cleveland | Klamath | Los Padres | Plumas | Shasta-Trinity | Stanislaus |
| Eldorado | Lake Tahoe BMU | Mendocino | San Bernardino | Sierra | Tahoe |